What Is Brain Death ? Communication Though Brain Between Individuals ? Research 2024
In this article we are going to explain some of question related to our brain . The question are as following :
- what is brain?
- How our brain works?
- How the data store in the memory and how is managed ? What happens when we imagine something?
- what happens with brain when we sleep?
- what is brain death ? Is this possible to share information through brain?
- In what format the data is store in the memory and how it retrieve ?
The list of question is not going to end. I think you have also some question that are not mention above but i believe if you read the full article then most of your question’s answer will you find.
The brain is a highly complex organ responsible for regulating bodily functions, processing sensory information, controlling emotions, storing memories, and enabling thought and imagination. Let’s break down your questions into clear sections.
What is the Brain?
The brain is the control center of the nervous system. It consists of billions of neurons (nerve cells) and glial cells, which support neuron functions. Different parts of the brain handle specific roles:
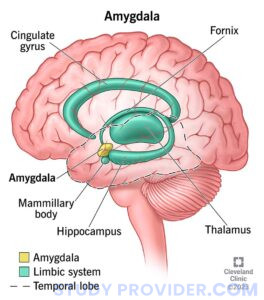
– Cerebrum: Controls voluntary actions, thinking, emotions, memory, and imagination.
– Cerebellum: Manages motor coordination and balance.
– Brainstem: Regulates involuntary functions like breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
How the Brain Works ?
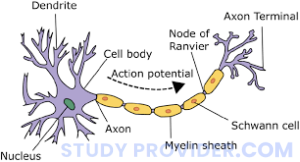
The brain communicates via electrical and chemical signals between neurons. These signals travel through synapses (connections between neurons), forming neural networks.
When we sense something (e.g., vision or sound), the brain translates it into electrical signals, processes the data, and makes decisions. Neurons store and transmit information across regions, such as the hippocampus (for memories) or prefrontal cortex (for decision-making).
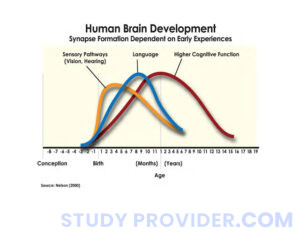
How the Brain Grows with Age ?
Brain growth occurs in several stages:
1. Early Childhood (Birth to 5 years) :
– Fastest brain growth happens here.
– Formation of new neurons and synapses peaks, supporting learning and language.
2. Adolescence:
– The brain prunes unnecessary synapses (removing weak connections).
– The prefrontal cortex (responsible for reasoning) matures last, often explaining impulsive behavior in teenagers.
3. Adulthood and Aging:
– Brain size stabilizes, but new neural connections continue forming through learning and experiences.
– Cognitive decline can occur in older age, but mental stimulation can slow it down.
How Imagination Works ?
When you imagine something, your brain activates similar neural patterns as when you experience it in real life.
– Visual Cortex: Engages when you picture objects or scenes.
– Prefrontal Cortex: Helps in combining experiences, memories, and ideas creatively.
– Hippocampus: Provides details from past experiences, even modifying them to form imagined scenarios.
The brain uses previous sensory inputs and experiences to create mental images, even in the absence of external stimuli.
Brain Function During Sleep :
During sleep, the brain performs essential functions:
1. Memory Consolidation: Information you learned during the day gets organized and transferred to long-term memory, especially during REM sleep.
2. Emotional Regulation: Sleep helps process emotions and reduce stress levels.
3. Neural Cleanup: The brain removes waste products, such as beta-amyloid (a protein linked to Alzheimer’s disease).
4. Dreams: In the REM phase, the brain replays and reorganizes fragments of past experiences, leading to dreams.
How Information is Stored in the Brain ?
Yes, everything you study, watch, or experience is stored in the brain. Here’s how and where it is stored:
Format : Information is stored in the form of neural connections. Learning strengthens certain synapses, while other connections weaken over time (synaptic plasticity). Memories are stored as patterns of electrical signals and synaptic weights.
Short-term Memory : Stored in the prefrontal cortex; lasts seconds to minutes (e.g., a phone number).
Long-term Memory : Stored across the hippocampus(for facts/events) and cerebral cortex (for skills/knowledge). Long-term memories are distributed, meaning different aspects of a memory—such as sounds or visuals—are stored in different regions.
How Much Can the Brain Store?
The brain’s storage capacity is estimated to be around 2.5 petabytes (2.5 million gigabytes)—comparable to millions of hours of television. However, this is not a strict number because:
– Memory retrieval depends on how often a memory is revisited or associated with other memories.
– Forgetting is a normal part of brain function to make room for more relevant information.
Summary
- Brain Structure: Controls body functions, thought, and emotion.
- Function: Uses electrical and chemical signals to transmit information.
- Growth: Brain grows rapidly during early childhood and continues developing through life.
- Imagination: The brain reactivates memory circuits to form mental images.
- Sleep: Essential for memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and neural maintenance.
- Storage: Memories are stored through neural patterns and synapses; the brain’s capacity is vast but selective.
I hope most of the question’s answer you find well . I know all the questions mention above is not discussed yet . We will discuses all the mention question in another article. If you have any question then comment below ,we will try to give you the answer of the question.so read the next article for more information.